In telecommunications, 5G is the fifth generation technology standard for broadband cellular networks, which cellular phone companies began deploying worldwide in 2019, and is the planned successor to the 4G networks, which provide connectivity to our current cellphones.
5G enables a new kind of network that is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together including machines, objects, and devices.That means quicker downloads, much lower lag and a significant impact on how we live, work and play. The connectivity benefits of 5G are expected to make businesses more efficient and give consumers access to more information faster than ever before.
5G represents a fundamental rearchitecture of the access network in a way that leverages several key technology trends and sets it on a path to enable much greater innovation. In the same way that 3G defined the transition from voice to broadband, 5G’s promise is primarily about the transition from a single access service (broadband connectivity) to a richer collection of edge services and devices.
How does it work?
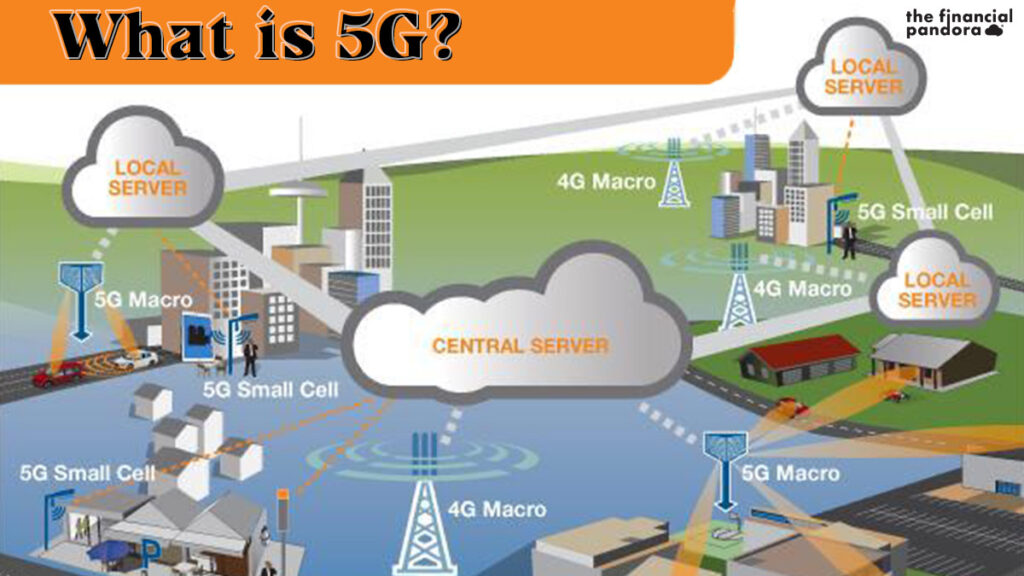
All wireless devices in a cell are connected to the Internet and telephone networks by radio frequencies (a.k.a – spectrum) to carry information through the air via a local antenna in the cell. 5G operates in the same way, but uses higher radio frequencies that are less cluttered. enabling it to carry more information at a much faster rate. These higher bands are called ‘millimeter waves’ (mmwaves).
To mitigate the hurdle of sending data over large distances and signal obstruction, 5G will utilise multiple input and output antennae to boost signals and capacity across the wireless network. The technology will also use smaller transmitters, placed on buildings and street furniture, as opposed to using single stand-alone masts. Current estimates say that 5G will be able to support up to 1,000 more devices per metre than 4G and will have greater bandwidth, giving higher download speeds, eventually up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbit/s)
5G technology will also be able to ‘slice’ a physical network into multiple virtual networks, to segment the network for a particular industry, business or application (Network Slicing). There are also plans to allow businesses to rent their own isolated and insulated network slice in order to separate them from competing Internet traffic. For 5G, the ‘core network’ is being redesigned to better integrate with the internet and cloud based services and also includes distributed servers across the network improving response times.
Where is 5G being used?
A defining capability of 5G is that it is designed for forward compatibility-the ability to flexibly support future services that are unknown today.
Not only will it Enhance our mobile broadband, it will also make our smartphones better, by ushering new immersive experiences such as Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality, with faster, more uniform data rates, lower latency, and lower cost-per-bit. In healthcare, 5G enable patients to be monitored via connected devices that constantly deliver data on key health indicators, such as heart rate and blood pressure. In automotive, 5G combined with Machine Learning-driven algorithms will provide information on traffic, accidents and introduce Autonomous Vehicles.
5G is meant to seamlessly connect a massive number of devices, with goods including refrigerators, lights, and even advertising hoardings being able to connect and communicate with one another, making almost every device “connected” and ‘smart.’ This will enable the growth of Internet of Things (IoT).
It will allow for the automation of logistics, material handling and factory automation via wireless technology and machine-to-machine communication, introducing “Smart Factories”. This will allow everything from material deliveries, through production, warehousing and the delivery of finished products to be controlled and monitored remotely. 5G will also offer improved remote working possibilities for employees and rural connectivity, allowing businesses to spur.
Impact on the Global Economy
Through Qualcomm’s Economy study, we found that 5G’s full economic effect will likely be realized across the globe by 2035, which include:
• $13.1 Trillion dollars of global economic output
• $22.8 Million new jobs created
• $265 Billion global 5G CAPEX and R&D annually over the next 15 years driving Global GDP growth by 10.8%
If 5G delivers everything it promises to, many expect the introduction of 5G to be a foundation for the fourth industrial revolution – Industry 4.0 – where everything is connected, processed and digitized. This can both transform and advance many existing industries, as well as create new ones.
5G in India
Department of Telecommunications recently announced that 5G trials are likely to begin in the next two to three months and trial schedule will be announced soon. They had been largely untouched by the public as the equipment to use them was largely inaccessible and expensive, but India’s telecom giants: Jio, Airtel and Vi (Vodafone-Idea) are all working with telecom gear manufacturers like Nokia and Ericsson to make 5G a reality in the country. Jio’s chairman, Mukesh Ambani, announced the company’s plans of building a 5G network made of indigenous hardware and technology components and Airtel has recently successfully trialled a 5G network in Hyderabad.
A huge reason behind the delay in the 5G rollout is the lack of cash flow, especially for Airtel and Vodafone-Idea due to tight market competition and low data-tariffs, compounded by exorbitantly high unit pricing for 5G networks. The parliamentary panel report on 5G in India, headed by Mr Shashi Tharoor, recommends the usage of 4G to continue in India for at least the next five to six years, which led to an auction kicking off in March for 4G networks and the 5G spectrum auctions being pushed back. So it seems like the early adoption of 5G in India will take another year and will be available to the masses in another three or four years.
Looking Forward
The applications of 5G will include everything from home appliances to industrial robots to self-driving cars, and it won’t just support humans accessing the Internet from their smartphones, but also swarms of autonomous devices working together on their behalf. There is more to supporting these services than just improving bandwidth or latency to individual users.
Albeit the fact that 5G is bound to change the way we consume information, entertainment and how we communicate with each other, the change will not happen overnight. We will need to switch to 5G compatible devices, new SIM cards and improved infrastructure, and the costs per unit may rise, but it is a giant technological leap which we must embrace. Unlike the prior generations, we hope India can ride the 5G wave and quickly implement the same in the near future.
For sources click here
This post was written in collaboration with Asif Yahiya Sukri LLP. Asif Yahiya Sukri LLP provides unparalleled personalized financial services to a broad range of clients across different geographical locations. With a presence in the USA, India and the MENA region, they ensure that all of your financial decisions are made carefully and with your best interests in mind. They are innovators who understand what goes into building companies.
You can also reach out to them on info@aysasia.com
Follow Us @
Sources
https://www.qualcomm.com/5g/the-5g-economy
https://www.indiatoday.in/technology/features/story/5g-in-india-are-we-there-yet-1769386-2021-02-15
https://www.qualcomm.com/news/onq/2019/10/01/whats-future-5g
https://telecom.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/5g-in-india-the-journey-is-about-to-begin/81671088
https://www.digit.in/features/internet/everything-you-need-to-know-about-5g-in-india-58457.html